Ever wondered why the Nordic Curl is gaining so much attention in the fitness world? This exercise isn’t just another trend; it’s backed by science for its impressive benefits in strengthening your muscles and protecting your joints. Let’s dive into why the Nordic Curl is a must-add to your workout routine.
Key Takeaways
-
1. Top Hamstring Activator: Nordic exercises, specifically the Nordic hamstring exercise with ankle dorsiflexion, achieved the highest hamstring activation among 114 different exercises examined in a systematic review. This makes it the best option for targeting the long head of the hamstrings.
2. Enhanced Hamstring Strength and Injury Prevention: Engaging in Nordic Hamstring Exercises (NHE) for 6–10 weeks significantly boosts hamstring eccentric muscle strength, leading to a reduction in injury rates and their recurrence, which is beneficial for athletes.
3. Improved Knee Joint Stability and Lower Limb Mobility: The Nordic Curl strengthens the knee joint and enhances its stability, making it less prone to injuries. It also improves lower limb mobility, which contributes to better athletic performance and reduced injury risk.
4. Effective Post-ACL Reconstruction Rehabilitation: For patients recovering from ACL reconstruction, incorporating Nordic Hamstring Exercises into their rehabilitation routines resulted in increased thigh circumference, higher peak torque in knee extension and flexion, and improved total work and average peak moment, indicating enhanced muscle performance and joint stability.
Understanding the Hamstring Muscles
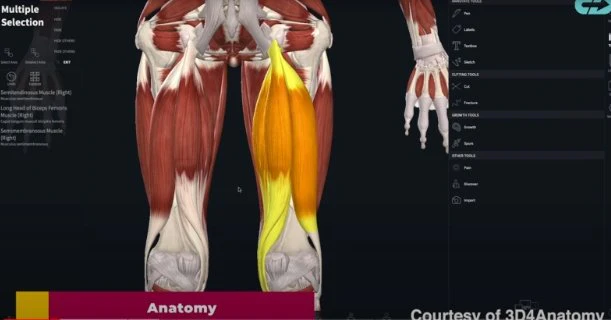
The hamstring muscles, specifically the semimembranosus, semitendinosus, and the long head of the biceps femoris are situated at the back of the thigh. These muscles are crucial in facilitating movement, enabling us to walk, run, and bend our knees. They are also key players in the primary actions of flexing the knee and extending the hip, which involves pushing the hips forward.
However, these muscles are not invincible. In fact, hamstring muscles are highly susceptible to injury, especially in sports that require sudden stops and starts, like soccer and football. Challenges arise when there are imbalances or improper forms during these primary actions, which can lead to common hamstring injuries. Therefore, understanding these muscles and how to train them effectively is crucial in mitigating injury risks.
What is the purpose of the hamstring muscles?
In addition to their role in knee flexion and hip extension, the hamstring muscles also serve a variety of other functions. They play a part in bending the knee joint, extending the hip joint, and even rotating the hip joint. These movements are fundamental to many of our daily activities, from walking to climbing stairs, making the hamstrings indispensable to our mobility.
However, the importance of these muscles extends beyond their functional roles. Strong hamstrings can contribute to overall muscle balance, potentially reducing the risk of injury in sports and physical activities. Therefore, incorporating hamstring workouts into your regular training routine can pay dividends in both performance and injury prevention.
The Importance of Hamstring Training
It is no secret that hamstring muscles are prone to injuries, including knee injuries, especially in sports. In fact, hamstring injuries make up approximately 37% of all soccer injuries, with a higher susceptibility among athletes involved in activities requiring sprinting or deep squatting positions like basketball, football, skiing, skating, and dancing. Factors contributing to these injuries include age, prior injuries, muscle fatigue, and muscle imbalances such as weak or tight hamstrings or quadriceps.
However, the good news is that these injuries are preventable. Studies show that including specific hamstring exercises, such as the Nordic Hamstring Exercise, can reduce injuries by up to 51%. Moreover, training the hamstrings appropriately leads to a more even distribution of load among leg muscles, which can reduce the risk of injury and boost overall performance in sports and active living. This goes to show that a well-rounded hamstring training routine plays a crucial role in athletic performance and injury prevention.
Why are Nordic Curls so Special?
In a recent systematic review of hamstring exercises, scientists were on a quest to find the best exercise for hamstring activation. They examined 3643 studies and 114 different exercises across 507 participants. The exercises they looked at included:
➡️ Bridges
➡️ Leg curls
➡️ Swings
➡️ Hip and back extensions
➡️ Good mornings
➡️ Hip thrusts
The verdict? Nordic exercises came out on top, achieving the highest hamstring activation. Specifically, the Nordic hamstring exercise with ankle dorsiflexion achieved the highest biceps femoris long head activation at 128.1% of its Maximal Voluntary Isometric Contraction. This suggests that Nordic exercises are the best option for activating the long head of the hamstrings, making them an effective choice for hamstring workouts.
This exercise, introduced by Mjolsnes et al. in 2004, is a self-weighted, eccentric movement that specifically targets the hamstrings. It has even been incorporated into the "FIFA 11+" program by the FIFA Medical Research Centre, a comprehensive warm-up regimen aimed at reducing injuries in athletes.
Evidence of Benefits
Enhanced Hamstring Strength and Reduced Injury Rates
Studies have shown that engaging in Nordic Hamstring Exercises (NHE) for 6–10 weeks significantly boosts hamstring eccentric muscle strength. This increase in strength is crucial because it directly translates to a reduction in injury rates and their recurrence. For athletes, this means fewer sidelining moments and more time in the game.
Improved Knee Joint Stability
One of the standout benefits of the Nordic Curl is its impact on knee joint stability. The exercise focuses on eccentric training, which activates the muscle in a controlled lengthening movement. This type of training is particularly effective in strengthening the knee joint, making it more stable and less prone to injuries. Improved knee stability is essential for athletes and active individuals, as it enhances overall performance and reduces the risk of sports-related injuries.
Enhanced Lower Limb Mobility
The Nordic Curl not only fortifies the knee joint but also improves lower limb mobility. This enhanced mobility is beneficial for a range of activities, from everyday movements to high-intensity sports. With better mobility, individuals can move more freely and efficiently, which contributes to better athletic performance and a reduced risk of injuries.
Start incorporating Nordic Curls in your home workouts with the Nordstick!
Research on Post-ACL Reconstruction Patients
A study focusing on patients who had undergone anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction revealed significant benefits from incorporating Nordic Hamstring Exercises into their rehabilitation routines. The study evaluated the effects of these exercises by measuring thigh circumference and using the Biodex System 3 Multi-Joint Isokinetic Testing System to assess knee joint extension and flexion strengths.
Key Findings
-
Increased Thigh Circumference: Patients who included Nordic Hamstring Exercises in their rehabilitation showed an increase in thigh circumference, indicating muscle growth and strength gains.
-
Higher Peak Torque (PT): These patients also demonstrated higher peak torque (PT) in knee extension and flexion at various angular velocities (60°/s and 120°/s). Peak torque is a measure of the maximum strength the muscle can exert, and higher values indicate stronger, more resilient muscles.
-
Improved Total Work (TW) and Average Peak Moment (AVG PT): The study also recorded improvements in total work and average peak moment, which further supports the effectiveness of Nordic Hamstring Exercises in enhancing muscle performance and joint stability.
Key Principles of Effective Hamstring Exercises
To achieve well-rounded hamstring development, it’s essential to focus on three key principles of effective hamstring exercises: compound movements, isolation movements, and eccentric training.
Let’s delve into each of these principles to understand their significance in hamstring training.
Compound Movements
Compound movements refer to exercises that involve multiple joints and muscle groups, enhancing overall strength development, coordination, and metabolic rate while also keeping your joints healthy. Some examples of compound movements include:
-
Deadlifts, which target and develop the hamstrings, glutes, and back
-
Squats, which work the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and core
-
Bench press, which engages the chest, shoulders, and triceps
-
Pull-ups, which activate the back, biceps, and shoulders
However, if you want to focus more intensely on specific muscle groups with less stress on other areas, there are alternative exercises you can try. For example, Romanian deadlifts are a variation of the traditional deadlift that primarily targets the hamstrings while putting less strain on the lower back.
Another compound movement that effectively targets the hamstrings is the good morning exercise. It provides an excellent method to add resistance in the hamstrings’ lengthened state while also working the glutes and creating significant time under tension. For beginners looking to build hamstring strength, the 45-degree hyperextension is also a suitable option.
Isolation Movements
Isolation movements, on the other hand, play a crucial role in focusing on specific hamstring muscles and addressing muscular imbalances. For instance, seated hamstring curls primarily target the inner side of the hamstrings (semitendinosus), while prone leg curls emphasize the outer hamstrings (biceps femoris).
When performing seated hamstring curls, it’s recommended to have an explosive concentric phase for 1 second, followed by a controlled eccentric phase over 3 seconds. For prone leg curls, maintaining a slow and controlled movement during the eccentric phase is key.
Lastly, to ensure efficient targeting of the hamstring muscles, it’s crucial to properly adjust the seated hamstring curl machine, setting the seat back so it ends just above the back of the knees.
Eccentric Training
Eccentric training involves exercises that enhance injury prevention and improve flexibility, such as Nordic hamstring curls. Nordic hamstring curls are performed to prevent injuries and improve overall athletic performance. The proper technique for this exercise includes maintaining a straight line from knees to shoulders, using the hands to catch oneself, and then pushing back up to the starting position.
When programming Nordic hamstring curls, it’s essential to focus on:
-
Eccentric muscle contraction, especially for reducing hamstring strain injury
-
Supramaximal exercise intensity
-
A minimum-effective dose
-
Increasing eccentric knee flexor strength
-
Increasing muscle fascicle length
Tips for Safe and Efficient Hamstring Training
Safe and efficient hamstring training involves a combination of:
-
Proper form, starting with bodyweight exercises
-
Incorporating warm-ups and cool-downs
-
Maintaining correct form in compound movements
-
Avoiding substituting form for weight or failing to work close enough to muscle failure
Starting with bodyweight in exercises like Bulgarian split squats and progressively adding weights can prevent injury and facilitate consistent progress in hamstring training.
Nordic Curls are considered as an advanced exercise, but you can achieve a full range of motion on your first try using OmniBands.
If you experience persistent hamstring tightness, shifting focus from stretching to strengthening may be necessary to accommodate overlengthened muscles. Incorporating cardio workouts can serve as a warm-up to prevent hamstring injuries or as part of a cool down to aid muscle recovery after intensive training.
The Role of Stretching and Mobility in Hamstring Health
In addition to strength training, regular hamstring stretching plays a crucial role in maintaining hamstring health. Stretching the hamstrings can lead to improved flexibility and mobility, thereby preventing lower back pain and reducing injury risk. Tight hamstrings can cause reduced pelvic mobility and place extra pressure on the lower back, but stretching can help alleviate this condition.
Regular hamstring stretching can enhance the range of motion in the hips, which facilitates daily activities such as walking and bending. To avoid tightness and improve flexibility, hamstring stretches should be performed 2 to 3 times per week as part of a balanced workout routine. A thorough warm-up, including 5 to 10 minutes of walking, is crucial for muscle preparation and injury prevention before any workout or stretching routine.
Summary
The Nordic Curl stands out as an effective exercise for enhancing hamstring strength and joint health. Understanding the hamstring muscles and incorporating a variety of exercises into your training routine can help prevent injuries and improve overall athletic performance. With the right balance of compound and isolation movements, eccentric training, and regular stretching, you can build strong, healthy hamstrings that support your active lifestyle.

Frequently Asked Questions
What are the hamstring muscles?
The hamstring muscles are comprised of the semimembranosus, semitendinosus, and the long head of the biceps femoris. They are located at the back of the thigh and are crucial for various movements such as walking, running, and bending the knees.
What is the purpose of the hamstring muscles?
The purpose of the hamstring muscles is to bend the knee joint, extend the hip joint, and rotate the hip joint. These muscles play a crucial role in various leg movements.
Why is hamstring training important?
Hamstring training is important because it reduces the risk of injury, corrects muscle imbalances, and improves athletic performance.
Why are Nordic curls considered effective?
Nordic curls are considered effective because they have been found to have the highest hamstring activation, making them an efficient exercise for targeting the long head of the hamstrings.
How can I create a balanced hamstring workout routine?
To create a balanced hamstring workout routine, incorporate a variety of hamstring exercises into your lower-body and full-body strength sessions and periodically increase the intensity of the exercises as your fitness level and goals evolve.
Sources:
-
Study on Hamstring Injuries: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3924636/
-
Research on Hamstring Muscle Activation: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/19417381211020330
-
Systematic Review of Hamstring Exercises: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphys.2019.01527/full
-
Effectiveness of Eccentric Training: https://journals.lww.com/nsca-jscr/Fulltext/2013/02000/Eccentric_Training_for_Hamstrings.20.aspx
-
Study on Compound Movements: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29196815/
-
Research on Isolation Movements: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5982014/
-
Benefits of Romanian Deadlifts: https://journals.lww.com/nsca-jscr/Fulltext/2015/02000/The_Effects_of_Heavy_Resistance_Training_on.16.aspx
-
Importance of Stretching for Hamstrings: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5304166/
-
Nordic hamstring exercises in functional knee rehabilitation after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a prospective, randomised, controlled study: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10624851/





































Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.